Literature
The FITS World Coordinate System standard (FITSWCS) defines
keywords and usage that provide for the description of astronomical
coordinate systems in a
FITS image header.
Electronic versions of the seven FITSWCS papers and related
background material are available:
| I: |
Representations of world coordinates in
FITS,
Greisen, E.W. & Calabretta, M.R., 2002,
Astronomy & Astrophysics, 395, 1061-1075.
|
| + |
Also a supplement to Paper I entitled
Concatenation
of FITS World Coordinate Systems by
Steve Allen and
Jessica
Mink.
|
| II: |
Representations of celestial coordinates
in FITS, Calabretta, M.R., &
Greisen, E.W., 2002,
Astronomy & Astrophysics, 395, 1077-1122.
|
| + |
Miscellaneous
notes on the derivation of some formulae and special
conditions in Paper II, dated 2004-02-11.
|
| III: |
Representations of spectral coordinates in
FITS,
Greisen, E.W., Calabretta, M.R.
Valdes, F.G., &
Allen, S.L.,
2006,
Astronomy & Astrophysics, 446, 747-771.
|
| + |
Errata dated
2013-09-21 for Papers I, II & III.
|
| IV: |
Representations of
distortions in FITS world coordinate systems,
Calabretta et al., draft dated 2004-04-22.
|
| V: |
Mapping on the HEALPix
grid, Calabretta M.R. & Roukema B.F.
2007,
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 381,
865-872. Describes the HEALPix projection and introduces
the HPX projection type in FITS.
|
|
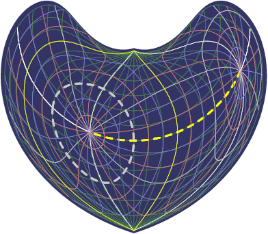
This diagram illustrating Bonne's
projection with conformal latitude +35° was produced by
WCSLIB, a C
implementation of the coordinate transformations defined in the
FITS WCS papers. The non-oblique native graticule is in dark
green.
The oblique 15° celestial graticule centred on celestial
coordinates (0°, +45°) with north celestial pole at
native coordinates (45°, 0°) is colour-coded blue, red
and white (in increasing order) with the equator and prime
meridian in yellow.
|
| VI: |
Representing the 'Butterfly'
Projection in FITS — Projection Code
XPH, Calabretta M.R. &
Lowe S.R. 2013,
Publications of
the Astronomical Society of Australia, 30, e050.
|
| VII: |
Representations of time coordinates in
FITS - Time and relative dimension in space,
Rots, A.H., Bunclark, P.S., Calabretta, M.R.,
Allen, S.L., Manchester, R.N., &
Thompson, W.T., 2015,
Astronomy & Astrophysics, 574, A36.
Introduction to celestial coordinate
systems; slides (in HTML) from a talk explaining FITS
world coordinate systems.
|
|
Software and test data
|
WCSLIB is implemented in
C, with support for FORTRAN via a set of wrapper functions. A
doxygen-generated
programming manual (HTML and
PDF) is provided.
NEW! (2025-12-06)
WCSLIB
8.5 contains a number of enhancements
and bug fixes. All older
releases of WCSLIB are also available.
As of release 8.5, WCSLIB's RCS version files are now included
in the distribution, thereby providing a documented history of
all changes made since v1.0.
WCSLIB was honoured with the
ADASS software
prize for 2025 for which I gave the invited conference talk
remotely by video.
A general curvilinear axis drawing routine,
PGSBOX, for
PGPLOT
that can optionally interface to WCSLIB, is also included with
WCSLIB.
Utility program HPXcvt is included with WCSLIB.
It converts 1D HEALPix pixelization data stored in a variety of
forms in FITS, including ring or nested organization in a binary
table extension, into a 2D primary image array with
HPX or
XPH coordinate representation.
An example
(13MiB bzip'd) is provided of its application to the
WMAP 3-year Internal Linear Combination map.
Example FITS files
produced for each of the projections in
Paper II and for a selection of
spectral representations from
Paper III, are available for testing
purposes.
|
|
